
In the international trading business, you may often hear the term “HS code”.
A HS code controls importing and exporting products by using specific codes,
and plays a role of seamless business trade in the world.
This time, we will explain the overview of the HS code, how the code is allocated, and when you will use it.
Video Annimation about HS Code in Logistics
The purpose of allocating HS code

There are variety of products which can be exported and imported in trading,
such as fresh products and industry products.
There are different specifications for industrial products, and there are countless varieties of products.
You may not be able to identify which type of products, only by checking the invoice,
or only by checking the product name on the packaging list.
However, by using HS code for customs declaration, you will be able to identify the product immediately.
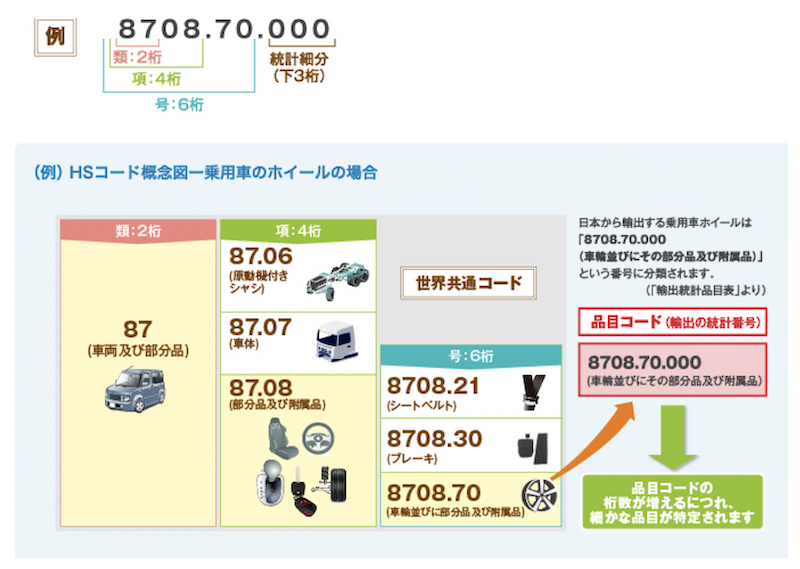
Example for HS Code
Let’s take a look at an example.
A wheel of a passenger car is classified with six digits as “8708.70”.
The HS code has a clear rule of how you classify the products.
Therefore, if you have the HS code information of “8708.70”, the customs will be able to
dentify what products are immediately.
Reference:The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry website
Regulation to control HS codes

So, how are HS codes rules and standards decided and controlled?
Universal code
The HS code is administrated by the World Customs Organization as,
“International Convention on the Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System” ,Which is HS Convention.
 Cat senior
Cat senior It’s called “Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System”!
The HS Convention is contracted to more than 150 countries, therefore this is a universal rule.
The HS code is reviewed every five years for product classification and amendments are updated. They may include more detail for specific products and new products may be added.
* Customs – Export Statistics Item List (2020 Edition)
Harmonized codes and country’s own code
Based on the classification and type of the product, the duty rate is decided. The codes are internationally harmonized, and the product type is shown with six digits when exporting and importing.。
More than six digits may be used to classify, and define products at more detailed level, based on each country’s domestic rules.
 Cat senior
Cat senior It is important that these 6 digits are common throughout the world!
HS Code classification method

First, let me explain detailed classification using HS code.
① Chapter, – first two digits
② Heading, – first four digits including the chapter
③ Sub-Heading, – first six digits including the chapter and the heading
The six digit classification is a universal code.
Now, let’s talk about how products are classified in detail.
HS code “Chapter”
Let’s take a look at the “Chapter”. There are 01 to 97 Chapters.。
First, they are roughly classified by products as follows.
Chapter 01: Live animals
Chapter 02: Meat and edible meat offal
Chapter 08: Edible fruits and nuts, peel citrus fruits or melon
Chapter 09: Coffee, tea, mate and spices
Chapter 10: Cereals
Chapter 11: Products of the milling industry, malt, starches, inulin, wheat gluten
Chapter 97: Works of art, collectors’ pieces and antiques
This is how products are classified within the 97 chapters.
Digits for Chapters allocated as follows, Chapter 1 is “01”, Chapter 2 is “02”,
Chapter 97 is “97”.
We will use the example of brown rice to check which HS code is allocated.
First, brown rice is a cereal, so it falls within Chapter 10.
 Cat senior
Cat senior Then, let’s see how “brown rice” is classified!
HS Code “Heading”
Next, the “Heading” classifies the Chapter in more detail.
Cereals are categorized as follows.
10.01,: Wheat and meslin
10.02,: Rye
10.03,: Barley
10.06,: Rice
The first four digits of HS code is 10.01.
Brown rice is rice, therefore it comes under 10.06.
HS “Sub-Heading”
Lastly, “Sub-Heading” categorizes what has been classified in the four digit, heading by product’ such as raw material and materials.
【Classification of chapter 10 (Cereal)】
10.04, : Oats
10.05, : Maize (Corn)
10.06, : Rice
10.07, : Grain sorghum
【Classification of Heading 10.06 (Rice) 】
10.06 – Rice
1006.10 – Rice in the husk
1006.20 – Brown Rice
1006.30 – Semi-milled or wholly milled rice
1006.40 – Broken rice
Therefore, brown rice Sub-Heading is 1006.20.
If the HS code is allocated as ten digits for brown rice, it will be displayed as “10.06.20.090.4” in Japan, for example.
Example of when the HS code is required.

I hope you understand what the HS code is by now.Now, when do you think HS codes are utilized?
Let’s take a look, with examples.
Import custom entry
HS codes are utilized for customs declaration for export and import for both countries.
Six digits for HS code classification is universal, however, different duty rates may occur in an exporting country and an importing country,depending on the understanding of classification of the product.
The duty rate may be different from what you have expected,
if import side customs specialists apply a different HS code for importing.
Selecting HS code by a customs specialist
When using an exporting and importing agency such as a freight forwarder,
there is normally a customs specialist who is qualified and will select the relevant exporting and importing goods’ HS code.
They will check the product name on the shipping note, and using their experience, select the relevant HS code.
However, when they are unable to identify the product by name, they need to confirm the details.
If it’s a chemical related product such as raw material, they need to check the material using the MSDS to identify its HS code.
 Seagull senior
Seagull senior This is also an occasional one…
The HS code which an exporter includes within the documentation, may differ from the HS code used by the customs specialist.
When HS codes do not match, the customs specialist will confirm the product detail and the ingredients,
with the exporter to ensure that the correct HS code is allocated.
It is also possible to confirm the correct HS code with customs, therefore when you are unsure, it is advised to contact customs. The HS code information will be declared to the customs, with the product name and once approved,
the relevant product code will be included on the export certification.
The role of a customs specialist is explained in another contents.
Please see this article for details on the work of customs officers.
What does a customs specialist do? You may wonder whether they use English, and whether they are tasked to reduce customs duty. If you are not involved the international logistics field, you may not be familiar with the role of the customs specialist, and you may not be able to understand the role. This time, …
Agreement of HS code by each country
When dealing with documentation such as invoices issued by exporters,
you will find HS codes along with the product name.
It is normally included, because when they process the import declaration in an importing country,
they are required to send the HS code in advance.
Individual countries have their own arrangement for allocating HS codes when importing.
24-hour Rule
When processing import customs clearance for EU countries and the USA, there is a 24 hours rule.
The HS code and detailed product information must be provided to the local customs,
24 hours before the cargo is loaded on the vessel.
A Certificate of Origin
When exporting products to a country which has EPA agreement,
you can receive a reduced custom tariff if you can provide a certificate of origin for the product.
If you are exporting with a certificate of origin, and the wrong HS code is applied,
the incorrect tariff rate could be applied and you may not receive the special rate.
 Cats and seagulls
Cats and seagulls If you make a mistake, you can’t do it…
A certificate of origin is submitted from an exporter to the Japan Chamber of Commerce and Industry.
Before submitting the documentation, you need to identify the 6 digits of HS code and tariff rate for the importing country.
According to the Japan Chamber of Commerce and Industry, HS code on a certificate of origin is not mandatory.
However, if there is any discrepancy relating to HS code, you will need to follow the importing country’s customs HS code decision.。
If an unexpected duty rate is applied, it may cause some problem between an exporter and an importer.
Normally, an exporting party will check with the importing party in advance,
and include the code on an invoice and a certificate of origin.
 Cat senior
Cat senior This is also occasionally found. ..
Please see this article for details on ertificate of origin here.
貿易や物流の仕事を必ず出てくる書類があります。それは原産地証明書です。既に貿易に携わっている人であれば「関税を安くするための書類でしょ??」と理解されているかもしれません。 実際にはその用途としての機能が強いのですが、今 …
Summary
Rules of HS codes are essential knowledge required in the worldwide trading industry.
You don’t need to know all products in depth classification, however it is important to understand the overview,
and how and why they are used to make arrangement for exporting and importing.
In the future, more countries may introduce the use of the HS code system, and the control will be strengthened.
It is important to understand the rule of HS code, as it provides additional protection and safety.









